Why nature is an engineer’s best inspiration
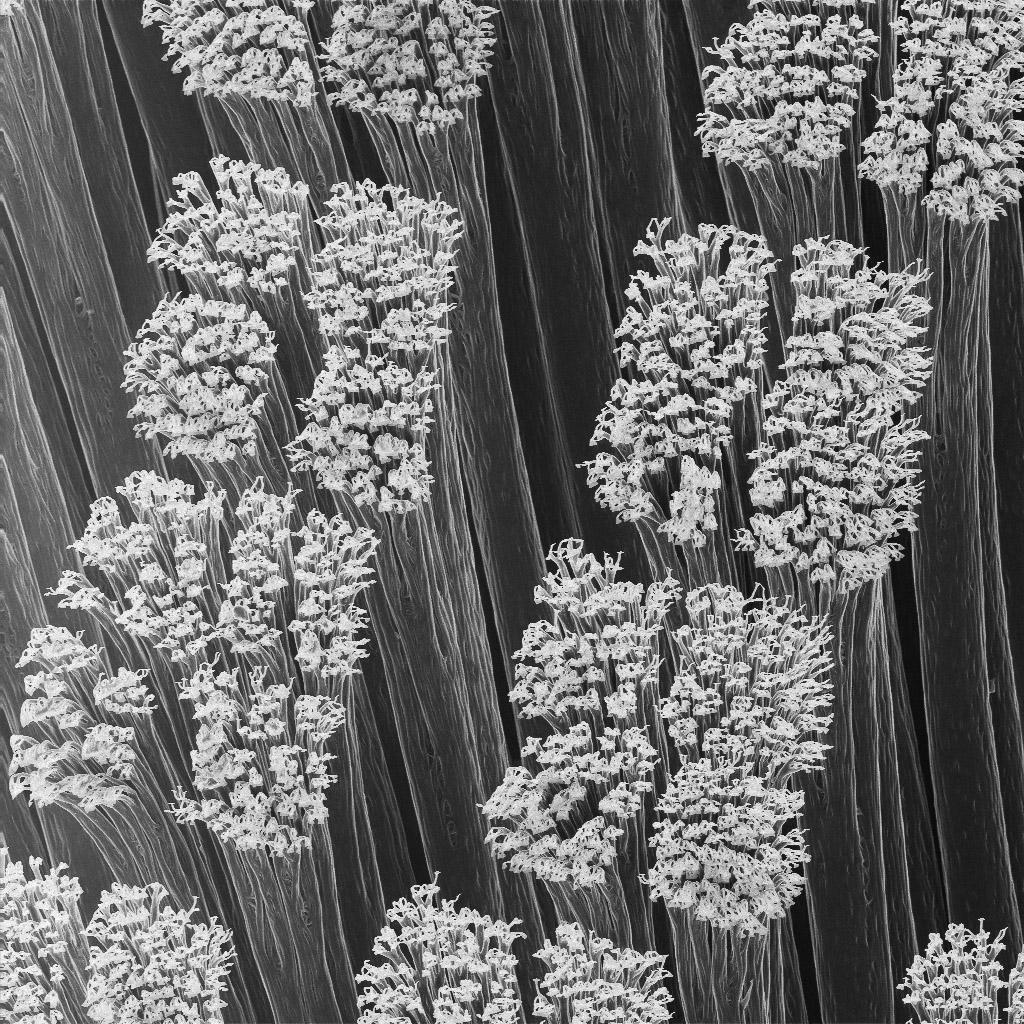
Gecko hairs. Each tip is only 200 nanometers wide.
Have you ever flown on a plane? Or used Velcro to hold two things together? If so, you’ve benefitted from biomimicry, an approach to solving human problems through nature-inspired innovations.
The invention of Velcro, for instance, happened one day when a man brought his dog into the house after a walk. The man noticed some burrs stuck to the dog's fur, and began studying their design and the way the burrs clung to fur and clothing using tiny hooks. Soon after, he invented the first strip of Velcro.
“Nature can be thought of as sort of a library of wonderful design ideas that can inspire us to design really wonderful new and better things,” says Robert Full, editor-in-chief of the journal Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, and professor of integrative biology at the University of California-Berkeley.
The Wright Brothers used biomimicry when they observed turkey vultures and subsequently designed airplane wings. Japanese bullet trains owe their technology to observations of kingfisher bills dragging through the water. And certain engineered paints were inspired by the incredible water-repellent, self-cleaning lotus leaf.
Hongrui Jiang, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, is inspired by animal eyes.
“I think the natural visual systems have some very interesting and intriguing designs," Jiang says.
Jiang has used many natural designs to inspire his engineering. In one case, he studied sunflowers to improve light collection on solar panels.
“We know that they can orient themselves throughout the day toward the sun to increase the sunlight interception. So, we developed the light sensitive polymers to actuate solar panels to track the sun for more electricity output.”
Other projects underway that are inspired by nature include materials similar to spider silk that are stronger than steel, more elastic than rubber and softer than wool. Or rescue robots that, like cockroaches, are able to compress themselves to fit in tight spaces while still running at high speeds — an invention engineers hope to send into buildings that might have collapsed after tornadoes, earthquakes or explosions.
“Looking at nature's designs can kind of free us from the constraints of our past design thinking and provide true innovation,” Full says. “I think this is a critically important point. If we don't preserve nature’s designs then the secrets will be lost forever. So if these seemingly useless species disappear, we'll never know what we've lost.
This article is based on an interview that aired on PRI's Science Friday.